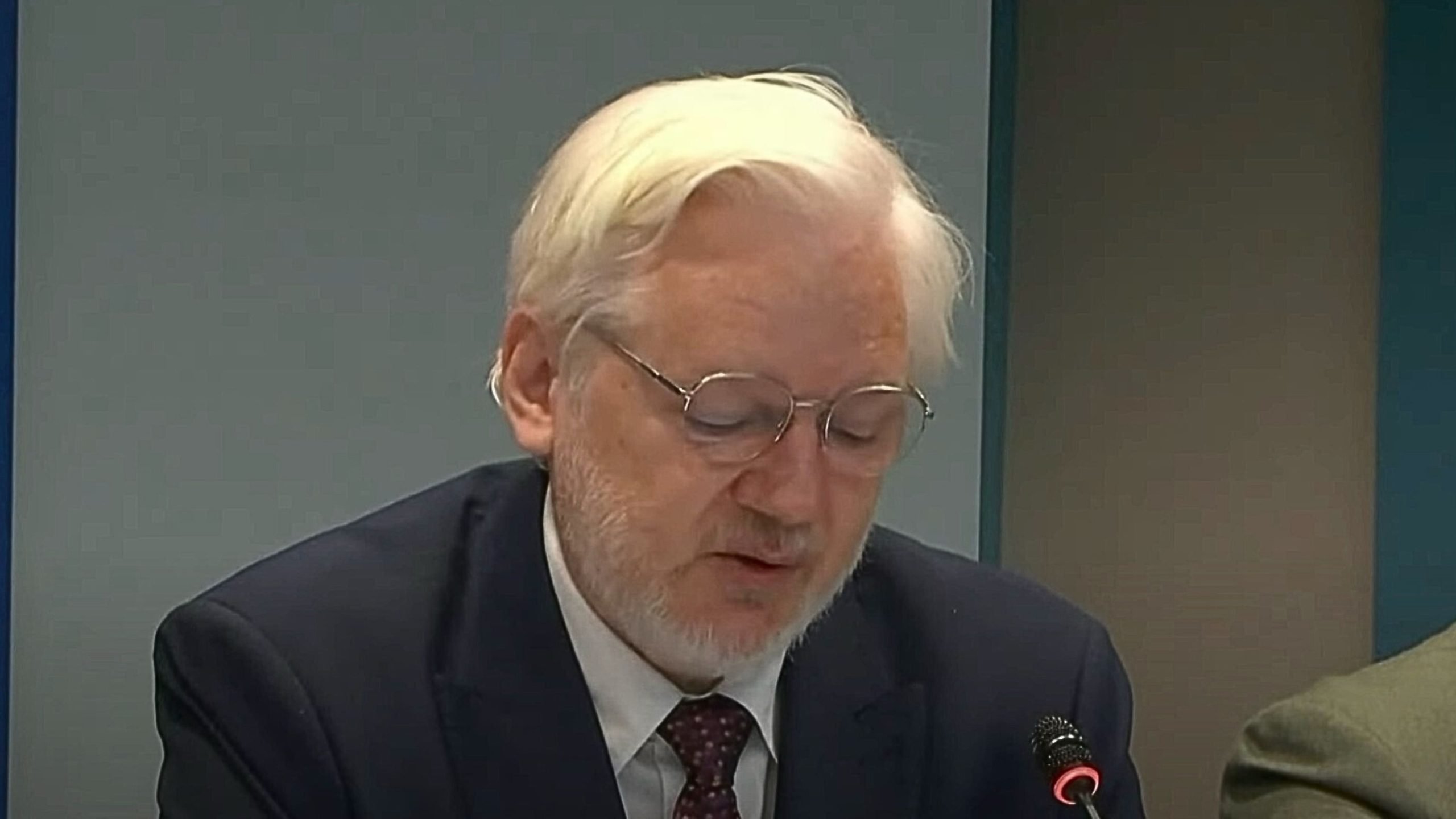
Julian Assange, now a free man, reflected on his long struggle for justice, describing his choice as one between freedom and “unrealizable justice.” In a plea to European lawmakers, Assange called for stronger protection of freedom of expression amidst increasing “impunity, secrecy, and retaliation for telling the truth.”
This marked his first public statement since a June plea deal ended nearly 14 years of imprisonment, confinement at an embassy, and house arrest in the UK. Assange’s message highlighted his disillusionment with the legal safeguards for journalists and whistleblowers, which he argued “only existed on paper” or failed to provide meaningful recourse. “I eventually chose freedom over unrealizable justice, after being detained for years and facing a 175-year sentence with no effective remedy,” he told the Council of Europe in Strasbourg today.
He continued, “I am not free today because the system worked. I am free today after years of incarceration because I pled guilty to journalism.” Assange was clear in his warning to European legislators that journalistic rights were under severe threat, saying, “The criminalization of news-gathering activities is a threat to investigative journalism everywhere.”
Related: Assange’s Plea: A Controversial End to a 14-Year Legal Struggle and the Impact on Free Speech
Assange became a figure of worldwide renown in 2010 after WikiLeaks published leaks from former soldier Chelsea Manning, revealing that US forces in Iraq had killed unarmed civilians, including Reuters employees. No one faced justice for these acts. Months later, Assange angered US authorities further by releasing 250,000 diplomatic cables, causing a diplomatic firestorm.
After years of legal battles, Assange walked free from a US district court in Saipan in June, following a plea deal where he admitted guilt to conspiring to obtain and release classified national defense documents. He received a 62-month sentence, effectively covered by his time served at London’s Belmarsh Prison.
The WikiLeaks founder spent five years in Belmarsh, preceded by seven years of refuge in the Ecuadorian embassy and more than a year under house arrest. British authorities arrested him in 2019 after Ecuador revoked his asylum, ending his nearly seven-year stay in their London embassy. Assange had initially taken refuge there in 2012, fearing extradition to the US via Sweden, where he faced allegations of sexual assault. Though Swedish prosecutors dropped the investigation in 2017, Assange remained in the embassy for two more years, worried about US extradition.
He also disclosed that his wife, Stella, and their then-infant son had suffered from US surveillance, including an alleged attempt to collect DNA from his baby’s diaper. Throughout the 90-minute address, seated beside his wife, Assange responded with composure, though he ultimately declined to answer a final question, citing exhaustion.
Reflecting on his experience, Assange described it as “profound and surreal” to transition from a cell in Belmarsh to appearing before European lawmakers. He struggled to convey the harshness of his isolation, remarking, “The experience of isolation for years in a small cell is difficult to convey. It strips away one’s sense of self, leaving only the raw essence of existence.”
The following day, European lawmakers were set to debate a draft resolution condemning the US’s actions. Drafted by Thórhildur Sunna Ӕvarsdóttir, an Icelandic MP with the Pirate Party, the resolution sharply criticized the misuse of the US Espionage Act, noting its “dangerous chilling effect” on publishers, journalists, and whistleblowers reporting governmental misconduct. It also criticized the UK for failing to defend Assange’s right to free expression.